The work environment is constantly changing, generating new risks that force those responsible for occupational risk prevention to propose new measures designed to minimize new forms of accidents. Similarly, advances in communications and technology help us to minimize and sometimes even eliminate certain risks that were previously difficult to avoid.
Technologies such as Artificial Intelligence have made it possible for machines to replace jobs with high mortality rates. Robots or exoskeletons can facilitate jobs, minimizing worker injuries. Thanks to drones, the risks of working at heights or in hard-to-reach areas can be avoided.
As William Cockburn, acting executive director of EU-OSHA, notes, "Between 1998 and 2019, non-fatal occupational accidents decreased by 58% in the EU, while fatal accidents decreased by 57%."
Evolution of the accident rate in the EU between 1998 and 2019.

Source: European Agency for Safety and Health at Work.
Several factors have contributed to this reduction: improved prevention measures, new working methods, training and awareness of workers and employers, etc. However, technological advances and the digitalization of the world of work have undoubtedly been determining factors.
Specialized software,
a fundamental tool in prevention
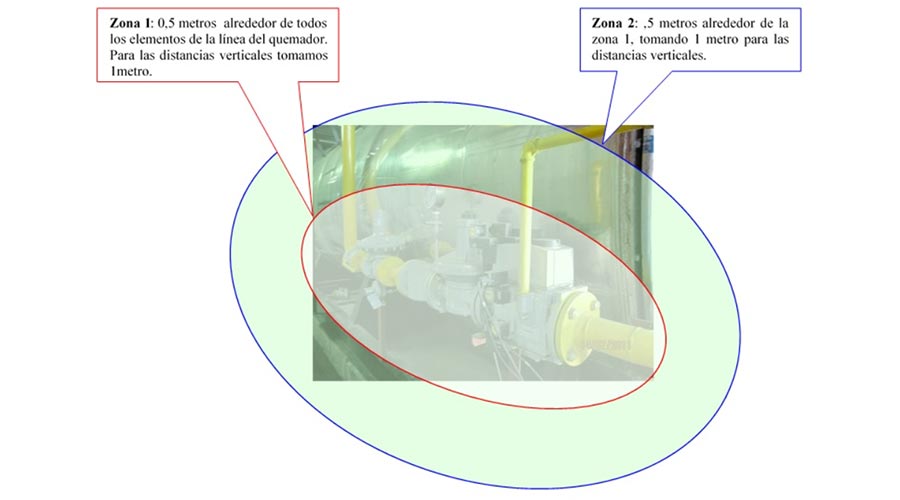

Specific occupational risk prevention applications and programs not only facilitate the work of technicians, but also provide increasingly accurate data analysis, allowing a better understanding of the causes of accidents and the aspects that need to be addressed in order to prevent them.
In this regard, the options are manifold. Governments have developed tools and applications for use in the various disciplines of occupational risk prevention: management, safety, hygiene, ergonomics, psychosociology and health programs. These computer tools are available to everyone on the websites of the occupational health and safety agencies (in Spain, the INSST).
Some of them, for example, make it possible to evaluate exposure to pollutants without the need to use environmental measurement equipment.
Ergonomics software helps to reduce worker injuries, as it allows better design of the workplace, analyzing inadequate postures, load handling or repetitive movements.
There are also chemical risk assessment programs and software for calculating the consequences of major accidents that can be used to estimate the damage to the population. Risk simulation programs (chemical, ATEX, fires, explosions, etc.) predict the behavior of the accident and the evolution of the threat and provide valuable information for the decision-making process.
CFD (computational fluid dynamics) modeling applied to ATEX is able to simulate situations that make it possible to predict the behavior of possible explosions in different processes and to evaluate the level of risk and damage that would occur, showing the results obtained in various real scenarios.
Image property of: Integral Prevention
Remote platforms and teleworking:
working from anywhere


Teleworking has been in use for years, but has been consolidated after Covid-19. Working remotely avoids millions of daily commutes and favors the reduction of accidents, since it reduces the risk of traffic accidents or accidents "in itinere".
However, teleworking can be considered a double-edged sword, since it carries a series of psychosocial risks such as the difficulty of separating personal life from the work environment or the excess of work generated by the obligation to be permanently connected to email, internet and social networks 24 hours a day, thus preventing rest and disconnection for the employee's well-being.
The use of remote networks and CAE platforms, on the other hand, facilitates the control of requirements and access to work centers with the prior uploading of the necessary documentation.
The evolution of equipment,
laboratories and ORP training
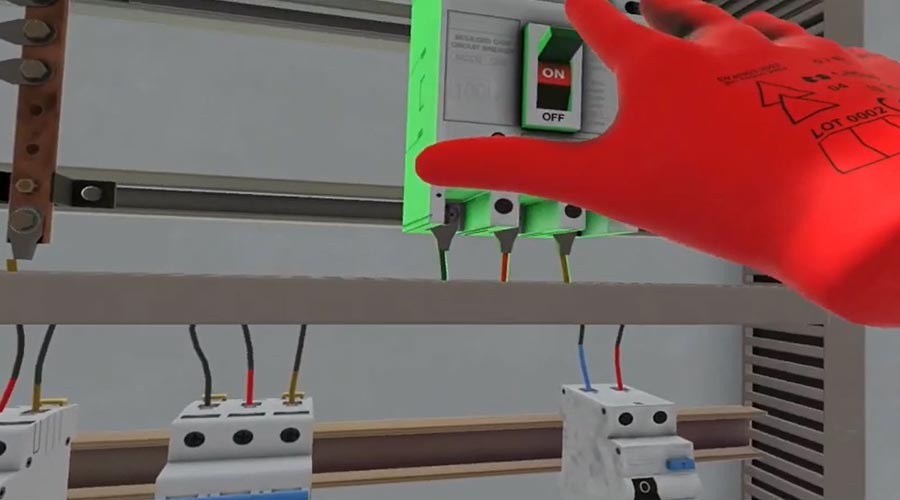

Technological progress related to occupational risk prevention is not limited to software and remote work. The constant evolution of measuring equipment, in addition to facilitating sampling strategies and the work of technicians, provides them with ever greater precision and makes it possible to detect contaminants that were previously undetectable, both in physical and chemical agents and in biological agents. The parallel evolution of analytical laboratories makes the results of measurements more complete and useful to prevent and improve the safety of working environments.
New technologies and digitalization have added new tools to occupational risk prevention training, such as online training platforms and virtual classrooms. But the real revolution comes from the use of virtual reality or augmented reality, which represents a qualitative leap in the student's learning experience. Virtual reality not only makes it possible to immerse students in real environments of danger, but also allows them to experience the consequences of their decisions.
In this scenario of continuous change, staff awareness and training must go hand in hand with technological advances, since new digital environments bring new risks or threats. For example, viruses, malware or phishing, unknown until recently, must be fought with cybersecurity and everyone must be involved in the process.
It is therefore vital that companies, unions and governments work together to adapt new technologies to the world of work, achieving safe working environments at all levels.
Styled
Title

